Disruption – a term that became synonymous with the fintech industry as it transformed how individuals and businesses do things financially.
In South Africa, fintech companies’ transformative changes span from individuals to businesses.
By allowing unbanked citizens (people with no access to traditional banks and financial services) to access financial services and providing alternative payment solutions to businesses, fintech in South Africa has facilitated monetary transactions within the border – boosting economic activities.
In this TRU Insight, you’ll explore how fintech in South Africa impacts economic growth and addresses wealth inequalities. Read on and understand fintech is becoming an emerging force in the global economy.
Fintech and Fintech Industry at a Global Scale
The internet was once a threat – not until it transformed how we do things for the better.
Fintech, or financial technology, emerged in the 1990s when personal computing and the internet were first introduced.
This transformative change pushed financial services companies to ride technological advancement to streamline their operations. While the adoption was long stretched, it made managing money, saving, and investing easier, more secure, and more efficient.
Now, fintech innovative solutions have become extremely significant in the digitalization of global economy.

Fintech’s benefits extend beyond developed economies. In fact, economies with high unbanked populations and financial service access are reported to benefit the most from the fintech industry.
One notable example is the South African economy, which is starting to embrace the fintech sector’s influence on its economic growth.
Fintech in South Africa: A Case Study in Inclusion and Economic Impact
Financial services are pivotal enablers for a country’s social and economic development.
Socially, they allow individuals to access financial products to meet their financial needs. Economically, such services provide small businesses with credit solutions for innovation and job creation.
These benefits ultimately facilitate the social and economic growth of the country.
However, traditional financial services hindered underbanked or underserved countries from enjoying such benefits.
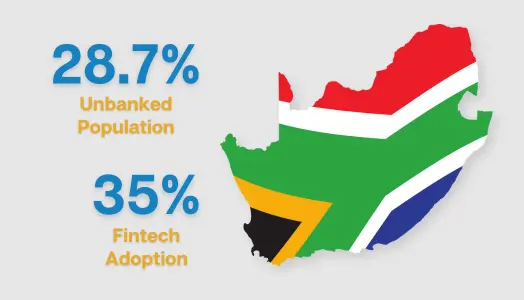
This is especially true in South Africa, where an estimated 28.7% of South Africans had no access to traditional banking or financial services.
But good things are coming in the country’s financial sector thanks to fintech adoption.
The South African Reserve Bank (SARB) acknowledged fintech’s contribution to the growth of the South African economy.
Essentially, the public is becoming more involved in the financial industry, and small companies are contributing to battle poverty through job creation.
Dive deep into why the rapid growth of fintech entailed the inevitable economic development of emerging markets.
It Provides an Opportunity to Address Wealth Inequality
South African citizens have been facing extended wealth inequality. In fact, the World Bank revealed that only 10% of the South African population has access to more than 80% of the country’s wealth.
In other words, 90% of South Africans share the remaining 10% (or less than) of wealth.
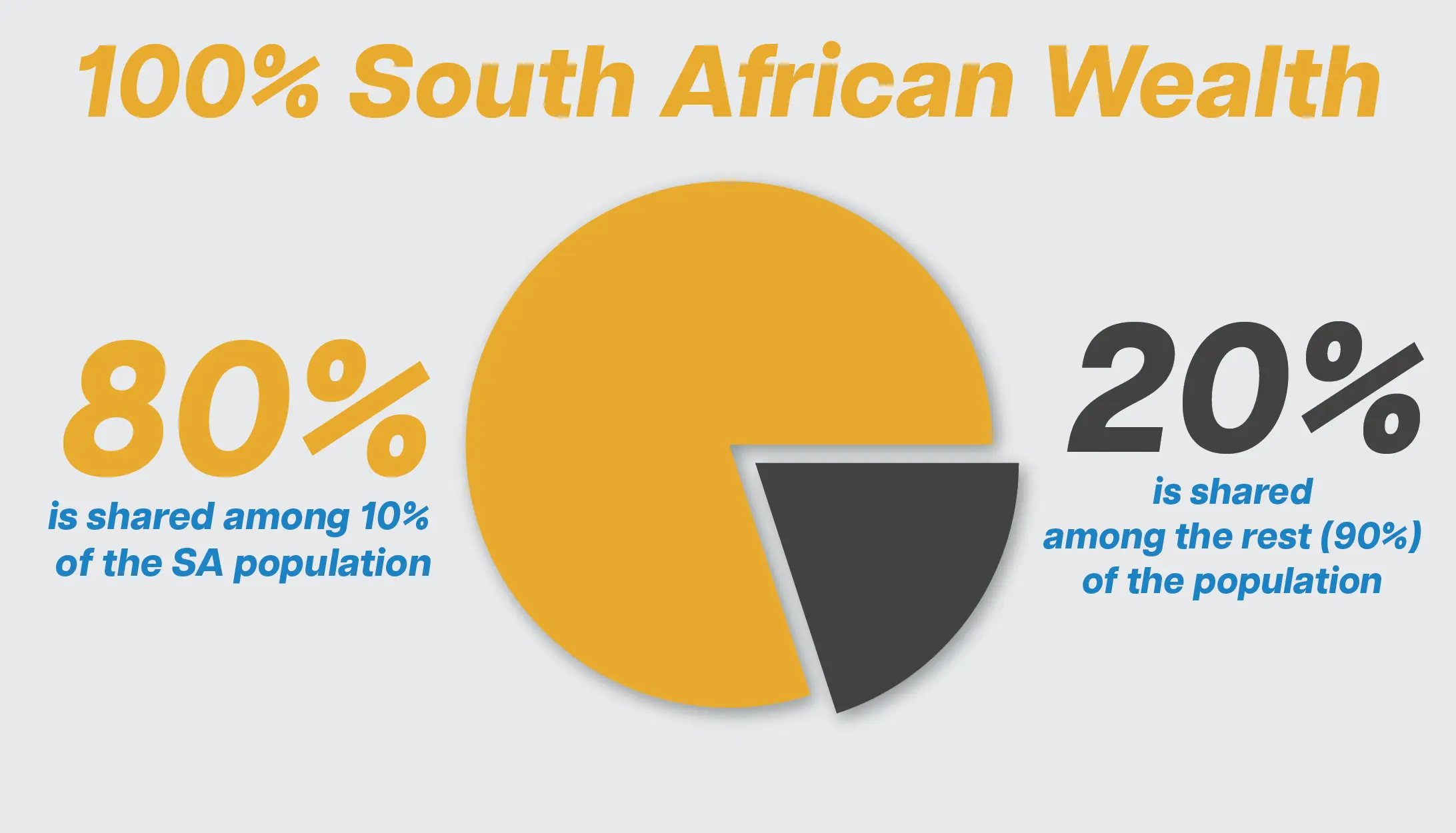
To address this, the SARB is taking action to embrace fintech services in the country fully. This effort is in partnership with the Financial Sector Conduct Authority and Financial Technology Association of South Africa.
This allows all South African citizens to access numerous financial products, including savings, lending, investment, and blockchain services, to grow their capital and potentially build wealth.
It Promotes Financial Inclusivity
Fintech bypasses the layered processes of traditional financial institutions, allowing individuals to have relatively easier access to financial services.
The World Economic Forum highlights that fintech simplifies and democratizes financial services through technology, offering bank-like services without the layered processes of traditional banks.
By breaking down barriers to financial access, fintech offers a lifeline to individuals and businesses traditionally excluded from banking systems. This particularly impacts people from lower-income backgrounds, rural areas, and those without a permanent address or regular income.
In South Africa, a significant portion of the country has remained unbanked.
However, the emergence of fintech allows financial services to be accessible to people from lower-income backgrounds in rural and remote areas.
According to the Fintech Association of South Africa (FINASA), fintech enables financial inclusion by reaching individuals in remote areas, without permanent addresses, working in the informal sector, or with little to no income.
It Boosts the Growth of Small Businesses
Fintech services are critical to the growth of startups and small businesses in emerging markets like South Africa.
According to Disrupt Africa, the increasing adoption of fintech innovation has become a key driver of entrepreneurship in the country.
By providing accessible credit and innovative payment solutions, fintech services bridge the gap between entrepreneurs and the funding they need to thrive.

Companies like iKhokha and Yoco have transformed payment processing, enabling small businesses to accept digital payments seamlessly.
And fortunately, there are more to come!
The SARB, FSCA, and FINASA revealed that more and more fintech startups are emerging with new technologies to make waves in the SA financial services industry.
It Presents Innovative Security Solutions
Users need assurance that their sensitive information and funds are secure.
Financial transactions are increasingly vulnerable to fraud and cyber threats in the digital age. Unfortunately, giant banking and financial institutions face growing technological challenges as their business models rely heavily on legacy systems.
The solution presented itself through the emergence of fintech companies and their sophisticated technologies.
By leveraging advanced encryption, artificial intelligence (AI), and blockchain technologies, these companies ensure safer transactions and protect users from potential threats.
- Advanced Encryption ensures that sensitive information (personal details and financial data) remains confidential and protected from unauthorized access.
- Artificial Intelligence analyzes transaction patterns and identifies anomalies to flag suspicious activities and prevent fraud before it occurs.
- Blockchain Technology provides a decentralized and fraud-proof ledger for recording transactions. This technology enhances transparency and security, making it difficult for cybercriminals to alter transaction records or commit fraud.
Ultimately, this boosts customer experiences, confidence, and participation in the financial system.
It Advocates Financial Literacy

A financially informed population is better equipped to build a better future for the country.
Many fintech platforms in South Africa include educational resources and tools to empower users with financial management and stability.
Additionally, fintech companies don’t only focus on wealth-oriented individuals like working professionals and adults. Instead, many fintech companies target young individuals to teach and cultivate early maturity in financial management.
The country has increasing adoption of fintech services’ whole new financial opportunities for the public, including:
- Investment services to save and grow money
- Lending services to borrow money
- Insurance services to safeguard financial future
Top Fintech Companies in South Africa
When discussing fintech disruption, the entities that usually come to mind are the leading Silicon Valley, downtown London, or other giants from powerhouse markets.
However, examining fintech companies through the lens of an emerging market helps you see their immense implications for the economy.
Let us look at the leading fintech companies in South Africa and how their operations contributed to the country’s recovering economy.
TymeBank

TymeBank is the first-ever digital bank launched in South Africa. In other words, it represents the country’s first step into the digitized financial service scene.
Launched in 2019, TymeBank has significantly contributed to financial inclusion in South Africa by providing affordable and accessible banking services to 7.4 million South Africans.
To make South Africa’s future financially capable, TymeBank provides banking services to young South Africans. According to the company, one of every five South Africans over 16 has a TymeBank account.
The company’s Series D funding round was in 2024. Led by Nubank, which raised USD 150 million, TymeBank secured USD 250 million through the recent funding series.
Tymebank valuation reached USD 1.5 billion.
Rand Merchant Investments

Rand Merchant Investment (RMI) is a prominent investment holding company in South Africa focused on the country’s financial sector.
It has significant stakes in various financial institutions, including:
- Discovery Limited
- OUTsurance
- Hastings Group Holdings
These three are giants in the South African financial industry, and RMI’s investment in them bolsters the country’s overall financial transactions.
RMI has also addressed the issue of unemployment in South Africa by investing in the business operations of financial institutions. These efforts of RMI contribute to the government’s initiative to battle poverty.
IG South Africa

IG prides itself on being the leading contract-for-difference (CFD) broker in South Africa. Through IG South Africa’s CFD brokerage service, the South African public can easily access the financial markets.
With its CFD service, South African investors can speculate on the price movement of financial assets like currency pairs, cryptocurrencies, company stocks, and commodities.
As South African investors access several trading instruments, they boost financial transactions within the country. They also stand a chance to grow their capital and secure wealth for a better financial future.
Aside from investment opportunities for the public, IG South Africa significantly boosted the country’s employment rate to address inflation.
The company addressed the devastating effect of the COVID-19 pandemic by expanding its business operations in Johannesburg. This resulted in a staggering 65% increase in the city’s workforce as IG created more than 40 jobs for the public.
Why Fintech Matters?
By disrupting traditional banking systems, fintech is leveling the playing field and making financial tools accessible to all.
Whether helping a small business secure funding or providing a rural farmer access to savings tools, fintech’s impact is far-reaching.

Fintech’s growth signals a brighter, more inclusive financial future where access is no longer a privilege but a right.
As it continues to evolve, the hope is that it will bridge the financial gap for millions worldwide, fostering resilience and driving economic progress.
The Challenging Fintech Regulatory Landscape
While fintech is driving economic growth, the regulatory landscape poses challenges.
With the help of the Financial Sector Conduct Authority and Fintech Association of South Africa, South Africa’s government must strike a balance between fostering innovation and ensuring consumer protection.
Policies to regulate fintech operations, particularly as public services face potential privatization, will significantly impact the industry’s trajectory.
Are Fintech Companies Reshaping Economic Growth?
The answer is a resounding yes.
Fintech companies are redefining financial access and empowering South Africans to participate more fully in the economy.
With fintech in the picture, managing your finances is no longer a privilege—it’s a right available to anyone with internet access.
However, remember that your hard-earned investment is at stake when you deal with fintech companies. Always stay informed by following their business development, regulatory compliance, and overall customer interaction.

















